The life cycle of a Spring bean is a fundamental concept in the Spring Framework.
Understanding the bean life cycle is crucial for effectively managing the behavior and state of beans within a Spring application.
A bean is simply an object managed by the Spring IoC container.
Instead of you instantiating and wiring up objects yourself, Spring does it for you.
But Spring doesn’t just create beans – it manages their entire life cycle.
- 1. Bean Life Cycle Overview
- 2. Detailed Walk Through of Each Phase
- 2.1 Plain Java Objects (No Spring Yet)
- 2.2 Letting Spring Manage Our Objects
- 2.3 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
- 2.4 Making Beans "Aware" of Their Context – The Aware Interfaces
- 2.5 BeanPostProcessor
- 2.6 Implementing Initialization and Destruction Callbacks
- 2.7 Modern Lifecycle Callbacks – @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy
1. Bean Life Cycle Overview
The Spring container manages the lifecycle of singleton-scoped beans.
Within this scope, Spring knows precisely when the bean is created, initialized, and destroyed.
For prototype-scoped beans, Spring is only responsible for creation.
Once the container creates the bean instance, it hands over management to the client code, and the Spring container no longer tracks its lifecycle.
Understanding the Spring lifecycle allows you to perform actions at specific points in a bean’s lifecycle.
These points can be many, but typically, actions are performed after the bean is initialized and before it is destroyed.
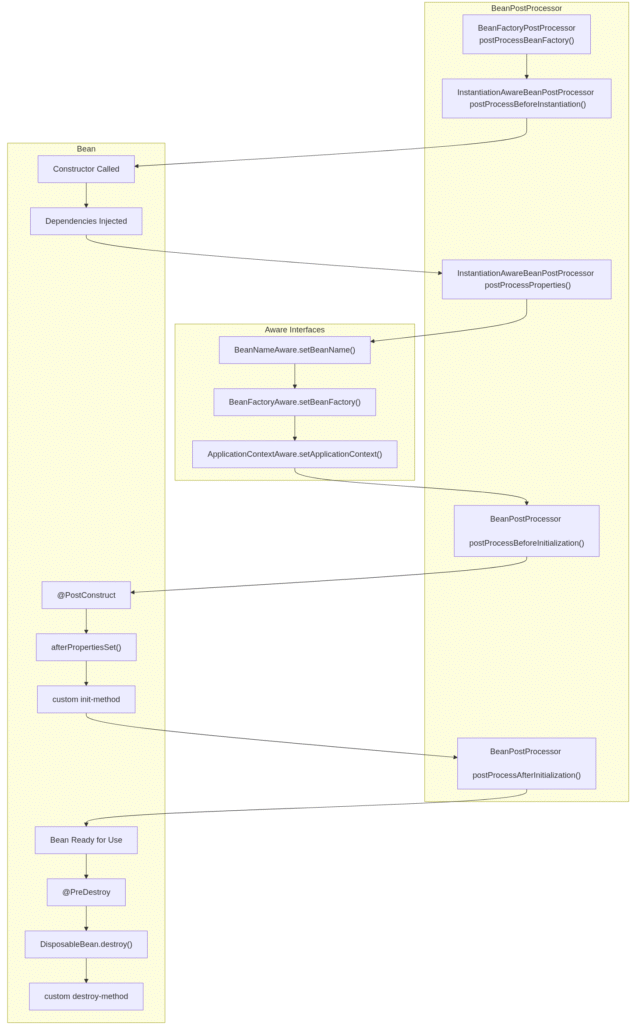
Below is the simplified flow of how a bean lives inside the Spring container :
- 1. Instantiation → Bean is created (constructor or factory method).
- 2. Dependency Injection → Properties and dependencies are set.
- 3. Aware Interfaces → Bean can access container-related information (BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware).
- 4. BeanPostProcessors → Custom logic before/after initialization.
- 5. Initialization → Special init methods (@PostConstruct, afterPropertiesSet(), etc).
- 6. Ready-to-use → The bean is fully initialized and available for business logic.
- 7. Destruction → Cleanup logic before the bean is removed (@PreDestroy, destroy()).
2. Detailed Walk Through of Each Phase
2.1 Plain Java Objects (No Spring Yet)
Before diving into Spring and its bean lifecycle, let us start with a very simple Java example.
We have two classes :
- Address : represents a city where the user lives.
- User : represents a user with a name and an associated address.
Both classes have constructors, setters, getters, and toString() methods.
To make things more illustrative, every method prints a message when it is called, so we can clearly see when and how each part of the object is executed.
package com.example19;
public class BeanLifeCycleExample {
static class Address {
private String city;
public Address() {
System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
}
public Address(String city) {
this.city = city;
System.out.println("\nAddress constructor with city called: " + city);
}
public String getCity() {
System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
}
}
static class User {
private String name;
private Address address;
public User() {
System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
}
public User(String name, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
System.out.println("\nUser constructor with name and address called: " + name + ", " + address);
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
return name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Address address = new Address("New York");
User user = new User("Alice", address);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
/*
Output:
Address constructor with city called: New York
User constructor with name and address called: Alice, Address{city='New York'}
User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
*/
2.2 Letting Spring Manage Our Objects
In the previous example, we created our objects manually with new.
Now, let us see how Spring can take over this responsibility and manage the lifecycle of our objects (called beans in Spring terminology).
1package com.example19;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
4import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
5import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
6
7public class BeanLifeCycleExample2 {
8 static class Address {
9 private String city;
10
11 public Address() {
12 System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
13 }
14
15 public Address(String city) {
16 this.city = city;
17 System.out.println("\nAddress constructor with city called: " + city);
18 }
19
20 public String getCity() {
21 System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
22 return city;
23 }
24
25 public void setCity(String city) {
26 System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
27 this.city = city;
28 }
29
30 @Override
31 public String toString() {
32 return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
33 }
34 }
35
36 static class User {
37 private String name;
38 private Address address;
39
40 public User() {
41 System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
42 }
43
44 public User(String name, Address address) {
45 this.name = name;
46 this.address = address;
47 System.out.println("\nUser constructor with name and address called: " + name + ", " + address);
48 }
49
50 public void setName(String name) {
51 System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
52 this.name = name;
53 }
54
55 public String getName() {
56 System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
57 return name;
58 }
59
60 public Address getAddress() {
61 System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
62 return address;
63 }
64
65 public void setAddress(Address address) {
66 System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
67 this.address = address;
68 }
69
70 @Override
71 public String toString() {
72 return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
73 }
74 }
75
76 public static void main(String[] args) {
77 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
78
79 BeanDefinition addressDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
80 .genericBeanDefinition(Address.class)
81 .addConstructorArgValue("New York")
82 .getBeanDefinition();
83 ctx.registerBeanDefinition("address", addressDef);
84
85 BeanDefinition userDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
86 .genericBeanDefinition(User.class)
87 .addConstructorArgValue("Alice")
88 .addConstructorArgReference("address")
89 .getBeanDefinition();
90 ctx.registerBeanDefinition("user", userDef);
91
92 ctx.refresh();
93
94 User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
95
96 System.out.println(user);
97
98 ctx.close();
99 }
100}
101/*
102 * Output:
103 * Address constructor with city called: New York
104 * User constructor with name and address called: Alice, Address{city='New York'}
105 * User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
106 */
Key parts of the code :
Create an ApplicationContext (line 77)
- This is the Spring IoC container.
- It is responsible for creating, wiring, and managing our beans.
Define bean metadata (line 79 – 90)
- Here we tell Spring to create an instance of the Address class and pass “New York” into the constructor when constructing it.
- Similarly, for the User.
- Notice how instead of passing the Address object directly, we give Spring a reference to another bean (address).
- Spring will resolve this dependency and inject it automatically.
Start the container (line 92)
- At this point, Spring looks at all registered bean definitions, creates the objects, injects dependencies, and prepares everything for use.
Retrieve the bean (line 94)
- Here we simply ask Spring for the User bean, and we get back a fully initialized object with its Address already set.
Close the context (line 98)
- Closing the context allows Spring to trigger the destroy phase of the bean lifecycle (important when resources need to be cleaned up).
2.3 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor is an interface in the Spring Framework that extends the BeanPostProcessor interface.
It provides additional hooks into the Spring bean lifecycle, allowing developers to intervene during the instantiation and property population phases of a bean’s lifecycle.
This interface is particularly useful when you need fine-grained control over bean creation, such as modifying bean properties before they are set or suppressing the instantiation of certain beans.
1package com.example19;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
4import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
7import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
8import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
9
10public class BeanLifeCycleExample3 {
11 static class Address {
12 private String city;
13
14 public Address() {
15 System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
16 }
17
18 public String getCity() {
19 System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
20 return city;
21 }
22
23 public void setCity(String city) {
24 System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
25 this.city = city;
26 }
27
28 @Override
29 public String toString() {
30 return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
31 }
32 }
33
34 static class User {
35 private String name;
36 private Address address;
37
38 public User() {
39 System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
40 }
41
42 public void setName(String name) {
43 System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
44 this.name = name;
45 }
46
47 public String getName() {
48 System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
49 return name;
50 }
51
52 public Address getAddress() {
53 System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
54 return address;
55 }
56
57 public void setAddress(Address address) {
58 System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
59 this.address = address;
60 }
61
62 @Override
63 public String toString() {
64 return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
65 }
66 }
67
68 public static void main(String[] args) {
69 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
70
71 // Register Address bean definition with property injection
72 BeanDefinition addressDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
73 .genericBeanDefinition(Address.class)
74 .addPropertyValue("city", "New York")
75 .getBeanDefinition();
76 ctx.registerBeanDefinition("address", addressDef);
77
78 // Register User bean definition with property injection
79 BeanDefinition userDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
80 .genericBeanDefinition(User.class)
81 .addPropertyValue("name", "Alice")
82 .addPropertyReference("address", "address")
83 .getBeanDefinition();
84 ctx.registerBeanDefinition("user", userDef);
85
86 ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(
87 beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
88 @Override
89 public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
90 throws BeansException {
91 if (beanClass == User.class || beanClass == Address.class) {
92 System.out.println(
93 "\n1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: "
94 + beanName);
95 }
96 return null;
97 }
98
99 @Override
100 public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
101 if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
102 System.out.println(
103 "\n2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: "
104 + beanName);
105 }
106 return true;
107 }
108
109 @Override
110 public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
111 throws BeansException {
112 if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
113 System.out.println(
114 "\n3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: "
115 + beanName);
116
117 System.out.println("Current PropertyValues: " + pvs);
118 }
119 return pvs;
120 }
121 }));
122
123 ctx.refresh();
124
125 User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
126
127 System.out.println(user);
128
129 ctx.close();
130 }
131}
132/*
133 * Output:
134 *
135 * 1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: address
136 * Address constructor called
137 * 2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: address
138 * 3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: address
139 * Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=1; bean property 'city'
140 * setCity called with: New York
141 * 1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: user
142 * User constructor called
143 * 2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: user
144 * 3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: user
145 * Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=2; bean property 'name'; bean property 'address'
146 * setName called with: Alice
147 * setAddress called with: Address{city='New York'}
148 * User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
149 */
Key additions in this example :
Property injection instead of constructor injection (line 74 81 82)
- Instead of passing constructor arguments, we now configure beans using property injection.
- This is useful because it lets us observe how Spring injects values after instantiation but before the bean is fully ready.
Adding a BeanPostProcessor (line 84 – 119)
- Here, we register an InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.
- Think of it as a hook into the bean lifecycle, allowing us to run custom logic at specific moments.
We override below methods in InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
- postProcessBeforeInstantiation : It is called before Spring creates the bean instance and we log a message whenever Spring is about to instantiate User or Address.
- postProcessAfterInstantiation : It is called immediately after the bean is created, but before its properties are set and it gives us a chance to inspect the “freshly constructed” object.
- postProcessProperties : It is called right before property values are applied to the bean so that we can see which properties Spring is about to inject and even modify them if we want.
2.4 Making Beans “Aware” of Their Context – The Aware Interfaces
Spring provides several callback-style interfaces that allow a bean to receive specific framework objects during initialization.
When a bean implements one of these interfaces, Spring automatically calls its corresponding setter method at the appropriate moment in the lifecycle.
Some of the most common ones are :
| INTERFACE | CALLBACK METHOD | PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|
| BeanNameAware | setBeanName(String name) | Gives the bean its own name as known by the Spring container. |
| BeanFactoryAware | setBeanFactory(BeanFactory factory) | Gives access to the BeanFactory that created it. |
| ApplicationContextAware | setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) | Provides access to the entire application context, allowing the bean to look up other beans or resources. |
By implementing these interfaces, beans can interact with the container that manages them – a key part of the Inversion of Control concept.
1package com.example19;
2
3import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
4import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
5import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
6import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
7import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
8import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
9import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
10import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
11import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
12import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
13import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
14
15public class BeanLifeCycleExample4 {
16 static class Address implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
17 private String city;
18
19 public Address() {
20 System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
21 }
22
23 public String getCity() {
24 System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
25 return city;
26 }
27
28 public void setCity(String city) {
29 System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
30 this.city = city;
31 }
32
33 @Override
34 public void setBeanName(String name) {
35 System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
36 }
37
38 @Override
39 public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
40 System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
41 }
42
43 @Override
44 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
45 System.out.println(
46 "\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
47 }
48
49 @Override
50 public String toString() {
51 return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
52 }
53 }
54
55 static class User implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
56 private String name;
57 private Address address;
58
59 public User() {
60 System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
61 }
62
63 public void setName(String name) {
64 System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
65 this.name = name;
66 }
67
68 public String getName() {
69 System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
70 return name;
71 }
72
73 public Address getAddress() {
74 System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
75 return address;
76 }
77
78 public void setAddress(Address address) {
79 System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
80 this.address = address;
81 }
82
83 @Override
84 public void setBeanName(String name) {
85 System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
86 }
87
88 @Override
89 public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
90 System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
91 }
92
93 @Override
94 public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
95 System.out.println(
96 "\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
97 }
98
99 @Override
100 public String toString() {
101 return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
102 }
103 }
104
105 public static void main(String[] args) {
106 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
107
108 // Register Address bean definition with property injection
109 BeanDefinition addressDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
110 .genericBeanDefinition(Address.class)
111 .addPropertyValue("city", "New York")
112 .getBeanDefinition();
113 ctx.registerBeanDefinition("address", addressDef);
114
115 // Register User bean definition with property injection
116 BeanDefinition userDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
117 .genericBeanDefinition(User.class)
118 .addPropertyValue("name", "Alice")
119 .addPropertyReference("address", "address")
120 .getBeanDefinition();
121 ctx.registerBeanDefinition("user", userDef);
122
123 ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(
124 beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
125 @Override
126 public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
127 throws BeansException {
128 if (beanClass == User.class || beanClass == Address.class) {
129 System.out.println(
130 "\n1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: "
131 + beanName);
132 }
133 return null;
134 }
135
136 @Override
137 public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
138 if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
139 System.out.println(
140 "\n2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: "
141 + beanName);
142 }
143 return true;
144 }
145
146 @Override
147 public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
148 throws BeansException {
149 if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
150 System.out.println(
151 "\n3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: "
152 + beanName);
153
154 System.out.println("Current PropertyValues: " + pvs);
155 }
156 return pvs;
157 }
158 }));
159
160 ctx.refresh();
161
162 User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
163
164 System.out.println(user);
165
166 ctx.close();
167 }
168}
169/*
170Output:
171 1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: address
172
173 Address constructor called
174
175 2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: address
176
177 3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: address
178 Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=1; bean property 'city'
179
180 setCity called with: New York
181
182 BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: address
183
184 BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
185
186 ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
187
188 1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: user
189
190 User constructor called
191
192 2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: user
193
194 3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: user
195 Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=2; bean property 'name'; bean property 'address'
196
197 setName called with: Alice
198
199 setAddress called with: Address{city='New York'}
200
201 BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: user
202
203 BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
204
205 ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
206
207 User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
208*/
In above code snippet, both Address and User implement :
- BeanNameAware
- BeanFactoryAware
- ApplicationContextAware
Each implementation logs when its callback method is invoked, and these messages let us trace exactly when in the lifecycle these callbacks occur.
2.5 BeanPostProcessor
This processor allows us to intercept beans both before and after their initialization phase, giving Spring a flexible mechanism to modify, wrap, or enhance beans.
It callbacks occur after all dependencies are injected and after the Aware interfaces have been called – that’s the point where the bean is almost fully ready.
package com.example19;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class BeanLifeCycleExample5 {
static class Address implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private String city;
public Address() {
System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
}
public String getCity() {
System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(
"\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
}
}
static class User implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private String name;
private Address address;
public User() {
System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
return name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(
"\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// Register Address bean definition with property injection
BeanDefinition addressDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(Address.class)
.addPropertyValue("city", "New York")
.getBeanDefinition();
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("address", addressDef);
// Register User bean definition with property injection
BeanDefinition userDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(User.class)
.addPropertyValue("name", "Alice")
.addPropertyReference("address", "address")
.getBeanDefinition();
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("user", userDef);
ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(
beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass == User.class || beanClass == Address.class) {
System.out.println(
"\n1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: "
+ beanName);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println(
"\n2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: "
+ beanName);
}
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println(
"\n3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: "
+ beanName);
System.out.println("Current PropertyValues: " + pvs);
}
return pvs;
}
}));
// Add BeanPostProcessor to show before/after initialization hooks
ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println("\n4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: " + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println("\n5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: " + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}));
ctx.refresh();
User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
ctx.close();
}
}
/*
Output:
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: address
Address constructor called
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: address
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: address
Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=1; bean property 'city'
setCity called with: New York
BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: address
BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: address
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: address
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: user
User constructor called
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: user
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: user
Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=2; bean property 'name'; bean property 'address'
setName called with: Alice
setAddress called with: Address{city='New York'}
BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: user
BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: user
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: user
User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
*/
Initialization happens between the two post-processor calls.
If we were to add @PostConstruct or implement InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet(), they would execute between these two post-processor phases.
postProcessBeforeInitialization()
- @PostConstruct
- afterPropertiesSet()
- custom init-method
postProcessAfterInitialization()
This is why the naming makes sense – the “before initialization” callback is invoked right before any init logic, and the “after initialization” callback is invoked right after it.
2.6 Implementing Initialization and Destruction Callbacks
InitializingBean and DisposableBean are two interfaces provided by the Spring Framework that allow beans to define custom initialization and destruction logic.
- afterPropertiesSet() : called after dependency injection and before the bean is ready for use.
- destroy() : called just before the bean is removed from the context.
In below code snippet, both User and Address implement InitializingBean and DisposableBean interfaces to define their own initialization and destruction logic.
package com.example19;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class BeanLifeCycleExample6 {
static class Address
implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String city;
public Address() {
System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
}
public String getCity() {
System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(
"\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("\nInitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet called for Address");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("\nDisposableBean#destroy called for Address");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
}
}
static class User
implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
private Address address;
public User() {
System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
return name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(
"\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("\nInitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet called for User");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("\nDisposableBean#destroy called for User");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// Register Address bean definition with property injection
BeanDefinition addressDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(Address.class)
.addPropertyValue("city", "New York")
.getBeanDefinition();
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("address", addressDef);
// Register User bean definition with property injection
BeanDefinition userDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(User.class)
.addPropertyValue("name", "Alice")
.addPropertyReference("address", "address")
.getBeanDefinition();
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("user", userDef);
ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(
beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass == User.class || beanClass == Address.class) {
System.out.println(
"\n1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: "
+ beanName);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println(
"\n2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: "
+ beanName);
}
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println(
"\n3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: "
+ beanName);
System.out.println("Current PropertyValues: " + pvs);
}
return pvs;
}
}));
ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println("\n4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: " + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println("\n5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: " + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}));
ctx.refresh();
User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
ctx.close(); // This will trigger DisposableBean#destroy for beans
}
}
/*
Output :
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: address
Address constructor called
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: address
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: address
Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=1; bean property 'city'
setCity called with: New York
BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: address
BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: address
InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet called for Address
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: address
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: user
User constructor called
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: user
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: user
Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=2; bean property 'name'; bean property 'address'
setName called with: Alice
setAddress called with: Address{city='New York'}
BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: user
BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: user
InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet called for User
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: user
User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
DisposableBean#destroy called for User
DisposableBean#destroy called for Address
*/
The method afterPropertiesSet() runs between the beforeInitialization and afterInitialization phases.
This confirms it belongs to the initialization step, just before the bean becomes “ready.”
At the end of the program, we call context.close() to trigger the destruction phase.
When the application context shuts down, Spring triggers the destruction callbacks.
This ensures any resources held by the bean – database connections, file handles, thread pools … are released cleanly.
2.7 Modern Lifecycle Callbacks – @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy
Spring offers a modern, annotation-based approach to initialization and cleanup using Jakarta EE annotations :
- @PostConstruct : runs after dependency injection, before the bean is ready for use.
- @PreDestroy : runs just before the bean is destroyed.
These annotations are part of Jakarta Annotations (jakarta.annotation), not Spring itself – meaning they are portable across frameworks.
package com.example19;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import jakarta.annotation.PreDestroy;
public class BeanLifeCycleExample7 {
static class Address implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private String city;
public Address() {
System.out.println("\nAddress constructor called");
}
public String getCity() {
System.out.println("\ngetCity called : " + city);
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
System.out.println("\nsetCity called with: " + city);
this.city = city;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(
"\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstructInit() {
System.out.println("\n@PostConstruct called for Address");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroyCleanup() {
System.out.println("\n@PreDestroy called for Address");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{city='" + city + "'}";
}
}
static class User implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private String name;
private Address address;
public User() {
System.out.println("\nUser constructor called");
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nsetName called with: " + name);
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("\ngetName called: " + name);
return name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
System.out.println("\ngetAddress called: " + address);
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
System.out.println("\nsetAddress called with: " + address);
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("\nBeanNameAware#setBeanName called: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("\nBeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: " + beanFactory.getClass());
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println(
"\nApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: " + applicationContext.getClass());
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstructInit() {
System.out.println("\n@PostConstruct called for User");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroyCleanup() {
System.out.println("\n@PreDestroy called for User");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "\nUser [name=" + name + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// Register Address bean definition with property injection
BeanDefinition addressDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(Address.class)
.addPropertyValue("city", "New York")
.getBeanDefinition();
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("address", addressDef);
// Register User bean definition with property injection
BeanDefinition userDef = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(User.class)
.addPropertyValue("name", "Alice")
.addPropertyReference("address", "address")
.getBeanDefinition();
ctx.registerBeanDefinition("user", userDef);
ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(
beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (beanClass == User.class || beanClass == Address.class) {
System.out.println(
"\n1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: "
+ beanName);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println(
"\n2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: "
+ beanName);
}
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println(
"\n3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: "
+ beanName);
System.out.println("Current PropertyValues: " + pvs);
}
return pvs;
}
}));
ctx.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(beanFactory -> beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println("\n4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: " + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof Address || bean instanceof User) {
System.out.println("\n5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: " + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}));
ctx.refresh();
User user = ctx.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
ctx.close(); // This will trigger @PreDestroy for beans
}
}
/*
Output :
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: address
Address constructor called
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: address
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: address
Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=1; bean property 'city'
setCity called with: New York
BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: address
BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: address
@PostConstruct called for Address
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: address
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation called for: user
User constructor called
2.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation called for: user
3.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties called for: user
Current PropertyValues: PropertyValues: length=2; bean property 'name'; bean property 'address'
setName called with: Alice
setAddress called with: Address{city='New York'}
BeanNameAware#setBeanName called: user
BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory called: class org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext called: class org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
4.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization called for: user
@PostConstruct called for User
5.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization called for: user
User [name=Alice, address=Address{city='New York'}]
@PreDestroy called for User
@PreDestroy called for Address
*/
In above code snippet, no need to implement interfaces like InitializingBean or DisposableBean.
By using @PostConstruct and @PreDestroy annotations, Spring automatically detects these annotations and invokes the corresponding methods at the correct lifecycle phases.

